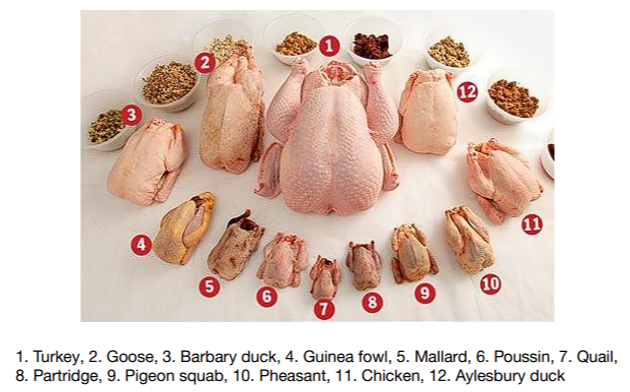
What is Poultry?
- Domesticated birds that are raised for meat
- Chickens are the most popular
- Poultry is especially useful because meats and eggs are consumed

Classification of Poultry
- Most US consumers prefer breast meat
- Generations of genetic selection lead to the creation of broad breasted turkey varieties that have rapid growth rates and high feed efficiency